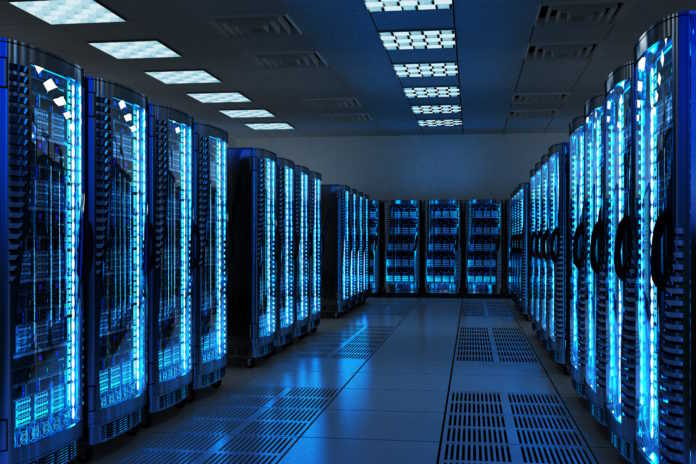
A data center is a facility that uses complex network, computing, and storage infrastructure to provide shared access to applications and data. This ensures both data safety and availability.
A data center consists of networked computers, storage systems, and computing infrastructure. It is used for processing, storing, and sharing, accessing, and processing large amounts of data across an organization, the physical infrastructure to support data processing and data communication, and utilities such as cooling. Electricity, network security access, uninterruptible power supplies.
It consists of cables, switches, routers, and firewalls that connect servers to manage huge amounts of data without compromising system performance. As a shared space for an organization’s IT operations, maintaining consistent performance is critical.
4 Types of Data Center Products
When it comes to data centers, one size does not fit all. Data center needs vary based on their construction, physical limitations, density requirements, and more.
Below are four common data center types:-
- Onsite data center
- Colocation data center
- Hyperscale data center
- Edge data center
Enterprise Data Center
An on-site data center, also called an enterprise data center, is located within a company’s site. It can be modified or expanded according to your company’s needs and is easily accessible for general maintenance and troubleshooting. Equipment is stored at the company’s location for better performance. This generally keeps your data safe and controlled by the company itself.
This data center is designed solely to support a single organization and is a highly private facility. The location can be on-premises or off-premises, depending on the consumer’s convenience. Corporate facilities are recognized by their ownership and purpose relative to their size and capacity. Perfect for businesses with unique network requirements and significant revenue streams to take advantage of economies of scale.
Colocation Data Center
Colocation data centers rent space from other companies. Many companies use this facility. This data center is designed solely to support a single organization and is a highly private facility. The location can be on-premises or off-premises, depending on the consumer’s convenience.
There are two types of colocation data centers.
- Retail
- Wholesale
Retail Colocation Data Center
Retail colocation data center rental space is small and only infrastructure equipment such as racks can be rented. We also maintain switchgear, generators, chillers, uninterruptible power supplies, and other equipment that keeps the location up and running.
Wholesale Data Center
Wholesale data centers rent entire data center units and offer larger spaces. These are suitable for businesses that need a lot of space and may expand in the future.
Hyperscale Data Center
Hyperscale data centers are large facilities built by companies with enormous data processing and storage needs. These data centers are very agile and the load can be easily managed. Computing power increases, and adding machines increases power. Common examples of companies using hyperscale data centers are Amazon, Google, and Microsoft.
Edge Data Center
Edge data centers are small distributed facilities that provide computing and storage close to where data is generated and used, and are small data centers located close to the edge of the network. It offers the same devices found in a traditional data center, but contained in a smaller size close to the user. It enables a wide range of applications and offers customers the benefits of lower latency, higher security, and greater control over their data.
Research suggests that edge data centers provide generous support for segmentation, increase processing power, and improve customer experience. For entering the local market or improving the performance of regional networks, these facilities are not only useful, but invaluable.
Conclusion
Over the past few years, data has become an integral part of organizations and a critical resource. The whole world works and functions through data. Data storage is therefore an equally important requirement in the management and use of data. A data center performs the task of storing data.
It is also a centralized facility that houses an organization’s critical applications along with critical data. The size and design of data centers rely on robust computing network and storage resources that validate and enable delivery of shared applications and data.
So you could say they run our lives just fine.